-
Buy Provigil (Modafinil) 200mg Online
Buy Provigil (Modafinil) 200mg online without prescription. Purchase Provigil (Modafinil) 200mg online without prescription .
-
Price range: $40.04 through $159.00
-
Buy Clonazolam Pellets 1mg online
Formal Name – 6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-8-nitro- 4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]benzodiazepine CAS Number – 33887-02-4Molecular Formula – C17H12ClN5O2Formula Weight – 353.8Purity – ≥98%Price range: $57.06 through $209.23 -
Buy Ativan 1MG
LORAZEPAM – ORAL (lor-AYE-zeh-pam)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Ativan
Buy Ativan 1mg Online – Effective Anxiety Relief and Insomnia Treatment | Chems Connect. Get fast-acting relief from anxiety and improve sleep quality with Ativan 1mg. This prescription medication promotes relaxation and is trusted by healthcare professionals. Order now for safe and discreet delivery.
Price range: $35.19 through $190.21 -
Buy Zolpidem Belbien Hemofarm 30 tablets
A box of Blien contains 30 tablets, each with 10mg of zolpidem tartrate. These Zolpidems are from the Hemofarm brand.$50.00 -
Buy XANAX 1mg Alprazolam 30 tablets
XANAX is a sedative and tranquilizer. It belongs to the benzodiazepine group. The active substance in Xanax is alprazolam. This product contains 1mg of alprazolam per tablet. One pack contains 30 tablets.
$70.00 -
Buy Temazepam 10mg 30 tablets
Order cheap online temazepam? Chemsconnect.com offers Temazepam for sale. Order easily through our website. 1 pack of temazepam 10mg contains 30 tablets. Would you prefer a stronger variant?
- Temazepam belongs to the drug category of benzodiazepines
- It works soothingly
- reduces anxiety and tension and weakens the muscles
- Often used in sleeplessness
- Do not drive a car after taking temazepam
$80.00 -
Buy Subutex (Buprenorphine) 8mg
- Molar mass: 467.64 g/mol
- CAS ID: 52485-79-7
- ChemSpider ID: 559124
- Formula: C29H41NO4
- Bioavailability: Sublingual: 30%; Intranasal: 48%; Buccal: 65%
- Excretion: Biliary and kidney
Price range: $309.00 through $769.00 -
Buy Suboxone 2mg
Suboxone 2mg is a reliable and effective medication for individuals battling narcotic addiction. Combining buprenorphine and naloxone, it helps alleviate withdrawal symptoms and cravings while reducing the risk of addiction. With Suboxone 2mg, you can take a step towards recovery and regain control of your life. Trust in this trusted solution prescribed by healthcare professionals. Experience the relief and support you need with Suboxone 2mg.
Price range: $299.00 through $649.00 -
Buy Pregabalin 75 mg 56 Capsules
Pregabalin 75 mg is a medication used for neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and partial-onset seizures in adults. It regulates brain activity to provide relief from pain and seizures. Available in oral capsules, it is taken as directed by a healthcare provider.
$80.00 -
Buy Methaqualone (Quaalude) 300mg online
Product Name: Methaqualone, Quaalude, Lemmon 714, Mandrax, Ludes
Dosage: Methaqualone 300mg
Imprints: “Lemmon 714”
Shape/Color: Round Milky White PillsPrice range: $123.61 through $810.00 -
Buy Lorazepam 2.5mg 30 tablets
Lorazepam is a sleep aid. It is soothing and relaxes the muscles. Each box contains 30 tablets of 2.5mg each.
$70.00 -
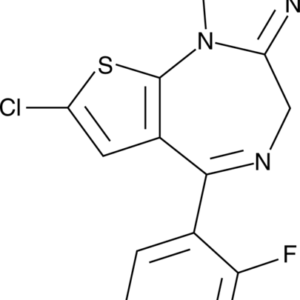
Buy Fluclotizolam 0.5mg Pellets
- Chemical Name: Fluclotizolam
- Systematic Name: 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]benzodiazepine
- Molecular Formula: C17H12ClFN4
- Molecular Weight: 326.76 g/mol
- CAS Number: [not assigned]
Price range: $150.00 through $990.00
Sleeping Pills: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Origins, Uses, and Dangers
Sleeping pills, also known as sedative-hypnotics, are medications designed to help individuals fall asleep or stay asleep. They are widely used to treat insomnia and other sleep disorders, but their misuse and long-term use can lead to significant health risks. This article explores the origins, uses, types, benefits, and dangers of sleeping pills, providing a thorough understanding of their impact on health and well-being.
What Are Sleeping Pills?
Sleeping pills are medications that promote sleep by acting on the brain and central nervous system. They are often prescribed for short-term relief of insomnia or other sleep-related issues.
Types of Sleeping Pills
Sleeping pills can be categorized into several types based on their chemical composition and mechanism of action:
- Benzodiazepines: Includes drugs like diazepam (Valium) and temazepam (Restoril), which enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter GABA to induce sleep.
- Non-Benzodiazepine Hypnotics: Includes drugs like zolpidem (Ambien) and eszopiclone (Lunesta), which are designed to have fewer side effects than benzodiazepines.
- Melatonin Receptor Agonists: Includes drugs like ramelteon (Rozerem), which mimic the effects of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.
- Antihistamines: Includes over-the-counter medications like diphenhydramine (Benadryl), which cause drowsiness as a side effect.
- Orexin Receptor Antagonists: Includes drugs like suvorexant (Belsomra), which block the action of orexin, a neurotransmitter that promotes wakefulness.
The Origins of Sleeping Pills
The history of sleeping pills is closely tied to humanity’s quest for better sleep and the development of modern pharmacology.
1. Ancient Sleep Remedies
Before the advent of modern medicine, people relied on natural remedies to promote sleep:
- Herbal Teas: Chamomile, valerian root, and lavender were commonly used to induce relaxation and sleep.
- Opium: Used by ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Greeks for its sedative properties.
2. The Birth of Modern Sedatives
The development of modern sleeping pills began in the 19th and early 20th centuries:
- Barbiturates: Introduced in the early 1900s, barbiturates were among the first synthetic sedatives. While effective, they carried a high risk of addiction and overdose.
- Benzodiazepines: Developed in the 1950s, benzodiazepines were considered safer alternatives to barbiturates and quickly became popular for treating insomnia.
3. The Rise of Non-Benzodiazepine Hypnotics
In the 1990s, non-benzodiazepine hypnotics like zolpidem (Ambien) were introduced. These drugs were designed to provide the benefits of benzodiazepines with fewer side effects and a lower risk of dependence.
How Do Sleeping Pills Work?
Sleeping pills work by targeting specific pathways in the brain to promote relaxation and induce sleep. The mechanism of action varies depending on the type of sleeping pill.
1. Enhancing GABA Activity
Many sleeping pills, including benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine hypnotics, enhance the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that slows down brain activity and promotes relaxation.
2. Regulating Sleep-Wake Cycles
Melatonin receptor agonists and orexin receptor antagonists work by regulating the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, helping individuals fall asleep and stay asleep.
3. Blocking Histamine Receptors
Antihistamines induce drowsiness by blocking histamine receptors in the brain, which are involved in promoting wakefulness.
Uses of Sleeping Pills
Sleeping pills are primarily used to treat sleep disorders, but they may also be prescribed for other conditions.
1. Treating Insomnia
Insomnia is the most common reason for prescribing sleeping pills. These medications can help individuals:
- Fall asleep faster
- Stay asleep longer
- Improve overall sleep quality
2. Managing Jet Lag
Sleeping pills, particularly melatonin receptor agonists, are sometimes used to help individuals adjust to new time zones and manage jet lag.
3. Addressing Shift Work Sleep Disorder
People who work night shifts or irregular hours may use sleeping pills to regulate their sleep patterns and improve daytime alertness.
4. Treating Anxiety-Related Sleep Issues
Benzodiazepines and other sedatives may be prescribed to individuals with anxiety disorders that interfere with sleep.
5. Palliative Care
Sleeping pills are often used in palliative care to improve the quality of life for patients with terminal illnesses by promoting restful sleep.
The Benefits of Sleeping Pills
When used appropriately, sleeping pills can provide several benefits, including:
- Improved Sleep Quality: Helps individuals achieve deeper, more restorative sleep.
- Short-Term Relief: Provides immediate relief for acute sleep problems, such as those caused by stress or travel.
- Enhanced Daytime Functioning: Reduces fatigue and improves concentration and productivity during the day.
- Support for Mental Health: Alleviates sleep-related symptoms of anxiety and depression.
The Dangers of Sleeping Pills
While sleeping pills can be effective, their misuse and long-term use can lead to significant health risks.
1. Dependency and Addiction
Many sleeping pills, particularly benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine hypnotics, have a high potential for dependency. Prolonged use can lead to:
- Physical Dependence: The body becomes reliant on the medication to fall asleep.
- Tolerance: Higher doses are required over time to achieve the same effect.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Stopping the medication abruptly can cause rebound insomnia, anxiety, and other withdrawal symptoms.
2. Side Effects
Common side effects of sleeping pills include:
- Drowsiness and fatigue
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Dry mouth and throat
- Memory problems and confusion
3. Risk of Overdose
Taking too many sleeping pills or combining them with other sedatives, such as alcohol, can lead to overdose. Symptoms of overdose include:
- Slow or shallow breathing
- Unconsciousness
- Coma or death
4. Sleepwalking and Other Parasomnias
Some sleeping pills, particularly non-benzodiazepine hypnotics, have been associated with parasomnias, such as:
- Sleepwalking
- Sleep driving
- Eating or performing other activities while asleep
5. Long-Term Health Risks
Chronic use of sleeping pills has been linked to:
- Cognitive decline and memory problems
- Increased risk of falls and fractures, particularly in older adults
- Potential links to cancer and early mortality (though research is ongoing)
Alternatives to Sleeping Pills
For individuals seeking better sleep without the risks associated with sleeping pills, there are several alternatives:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
CBT-I is a structured, evidence-based approach to treating insomnia that focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors related to sleep.
2. Sleep Hygiene
Improving sleep hygiene can help promote better sleep naturally. Tips include:
- Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule
- Creating a comfortable sleep environment
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake
- Avoiding screens before bedtime
3. Relaxation Techniques
Practices like meditation, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
4. Natural Remedies
Herbal supplements like valerian root, chamomile, and melatonin may provide mild sleep-inducing effects.
5. Lifestyle Changes
Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management can improve overall sleep quality and reduce the need for sleeping pills.
Regulation and Safety of Sleeping Pills
The regulation of sleeping pills varies by country, but most governments have implemented measures to ensure their safe use.
1. Prescription Guidelines
Sleeping pills are typically prescribed for short-term use, with healthcare providers closely monitoring their effects and potential side effects.
2. Over-the-Counter Options
Some sleeping pills, such as antihistamines, are available over the counter. However, these medications should still be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
3. Public Education
Educational campaigns aim to raise awareness about the risks of sleeping pills and promote safer alternatives.
Tips for Using Sleeping Pills Safely
If you are prescribed sleeping pills, here are some tips to ensure safe and effective use:
- Follow Your Doctor’s Instructions: Take the medication exactly as prescribed and do not exceed the recommended dose.
- Use Short-Term: Avoid using sleeping pills for more than a few weeks unless directed by your doctor.
- Avoid Alcohol: Combining sleeping pills with alcohol can increase the risk of side effects and overdose.
- Be Aware of Side Effects: Monitor for any unusual symptoms and report them to your doctor.
- Plan for Adequate Sleep: Ensure you have enough time to sleep (7-8 hours) before taking a sleeping pill.
Conclusion
Sleeping pills have revolutionized the treatment of insomnia and other sleep disorders, providing relief for millions of people worldwide. However, their misuse and long-term use can lead to significant health risks, including dependency, side effects, and overdose.
By understanding the origins, uses, and dangers of sleeping pills, individuals can make informed decisions about their use. Through education, regulation, and the promotion of safer alternatives, we can ensure that sleeping pills are used responsibly to improve health and well-being.